INTRODUCTION
Budd-Chiari syndrome (BCS) is a clinical condition resulting from the blockage of the main hepatic veins or vena cava caudalis (1, 2). Nakamura et al. (3) determined membranous obstructions affected both vena cava caudalis and the hepatic veins. In 18% of cases, only the vena cava caudalis was affected, while the hepatic veins were affected in 10% of the cases. The blockages in the vena cava caudalis can be severe and may cause hepatocellular necrosis, hepatic failure, cirrhosis, and encephalopathy (4, 5). BCS is very rare in the literature and practice in domestic animals. Therefore, the aim of this case report was to describe Budd-Chiari syndrome in a cat, with mild clinical, ultrasonographic and laboratory findings, as well as treatment of affected cat. Laboratory findings were used to evaluate the effects of L-carnitine on liver and oxidative status of the cat.
CASE REPORT
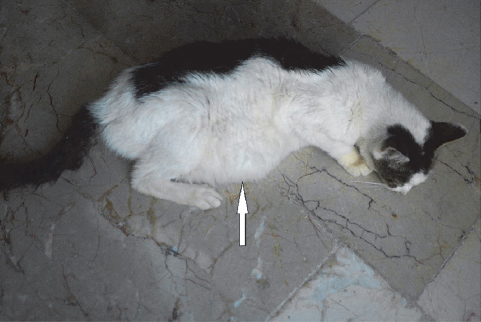
A 15 year-old female cat, with clinical sings of vomiting and severe abdominal distension was admitted at the clinic (Fig. 1).
Figure 1. A 15 year-old female cat with abdominal distension (white arrow)
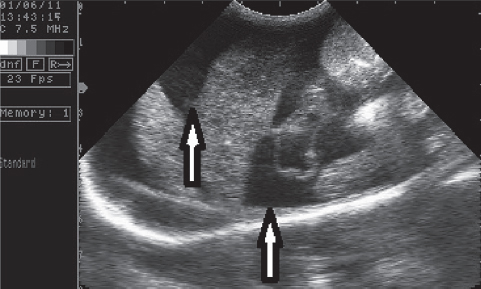
There was no history data of any trauma and infection with feline enteric coronavirus (FCoV). Polymerase Chain Reaction (conventional-PCR) on corona virus was negative. The clinical and the ultrasonographic examination revealed abdominal pain, hepatomegaly, ascites, and increased liver echogenicity (Fig. 2).
Figure 2. The ascites is seen in the anechoic area
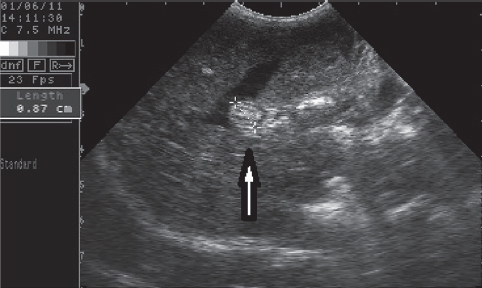
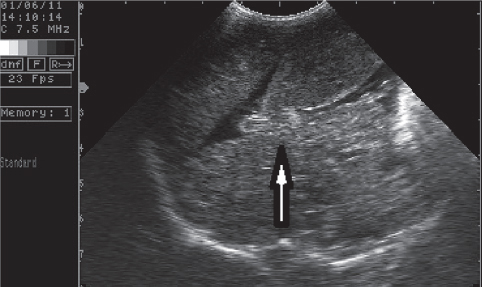
After the aspiration of abdominal fluid, a cytology smear was prepared and the fluid was described as modified transudate. Cytology findings in the cell population of the aspirated abdominal fluid described mesothelial cells, macrophages, non-degenerate neutrophils and small lymphocytes. A blockage of the vena cava caudalis at the intrahepatic region called Budd-Chiari syndrome was found with ultrasonographic examination. The location of the thrombus was confirmed by longitudinal and transversal cross-section. The thrombus was 0.87 cm in diameter at the junction of the hepatic vein and the vena cava caudalis (Fig. 3 and Fig. 4).
Figure 3. Enlarged vena cava caudalis from thrombosis (ventradorsal position-transversal cross-section)
Figure 4. Thrombosis of vena cava caudalis (ventradorsal position-longutidinal cross-section)
During this study, we proposed a hepatoprotective and lower salt diet (easy digestible foods with high quality protein and highly digestible protein; Prescription Diet® h/d®, l/d® feline-Hill’s Pet Nutriton). The following medical therapy was recommended: cefuroxime axetyl 25 mg/kg/body weight 10 days, furosemide 2 mg/kg body weight 10 days, and total 330 mg dosage L-carnitine. After fortnight of therapy, the cat’s appetite was increased and laboratory results got better as well. Obtained biochemical results are presented in Table 1. The amount of abdominal fluid in the cat was reduced as a result of the diuretic therapy; but the serum concentration of urea was elevated. A small amount of fluid was detected in the abdomen at the beginning of the therapy. After antibiotics and furosemide treatment, the L-carnitine administration was continued. In the following period, the amount of abdominal fluid increased again and unfortunately the cat died three months after the onset of the disease. The animal owner did not allow the necropsy.
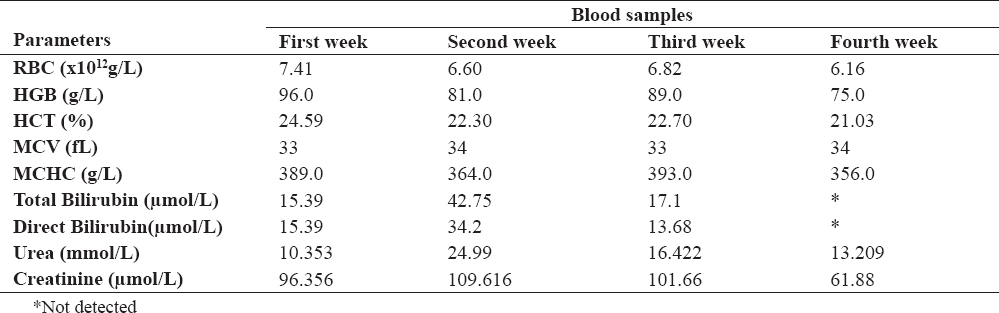
Table 1. Hematological findings in blood samples
A total of 5 ml blood samples were collected with venipuncture of vena cephalica antebrachi externa. Some biochemical (serum tubes with clot factor) and hematological (tubes for whole blood with EDTA) analyses were performed, such as liver transaminases alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), further gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT), total bilirubin, albumin, total protein, direct bilirubin levels, total antioxidant capacity status (TAS) and total oxidant status (TOS), in the serum samples. Furthermore, TAS and TOS in ascites fluid were examined.
Total antioxidant and oxidant capacities were determined colorimetrically (PowerWave XS, BioTek Instrument, Bedfordshire/UK) using a commercial kit (Rel Assay Diagnostic, Gaziantep, Turkey) as previously described by Durgut et al. (6). Serum TAC was determined using a novel automated measurement method developed elsewhere (7). The results are expressed as μmol of Trolox equivalent/liter. Total oxidant status levels were measured using commercially available kits (Rel Assay Diagnostic, Gaziantep, Turkey). The assay was calibrated with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and the results were expressed in terms of micromolar H2O2 equivalent per liter (μmol H2O2 equivalent/L) (8).
The levels of ALT and AST, total bilirubin and direct bilirubin in the serum sample were marked increased, with regards to the serum albumin and total protein concentration. Serum levels of urea and creatinine were in physiological range at the beginning of the therapy. There were no marked changes in the hematological parameters (Table 1).
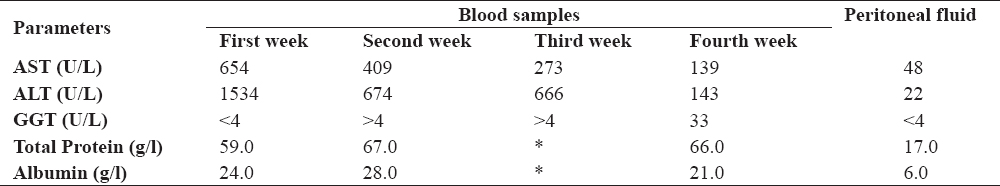
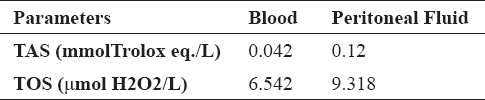
Concentrations of TAS and TOS were higher in the peritoneal fluid compared with the serum samples (Table 2 and Table 3). Concentration of enzymes was increased, particularly gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT).
Table 2. Biochemical findings in blood samples and peritoneal fluid
Table 3. TAS and TOS findings in blood samples and peritoneal fluid
DISCUSSION
This clinical case describes the ultrasonographic and laboratory examinations of BCS. The first case of hepatic vein stenosis, causing ascites and mild anemia in a cat was described by Schrope (9).
Humans with BCS, have a thin fibrous band or segmental fibro muscular membrane, formed in both supra hepatic areas (entrance of the hepatic veins and from the right atrium), as well as intrahepatically (in the liver) and in the vena cava inferior (1, 3, 10). A membranous obstruction of the inferior vena cava known as idiopathic Budd-Chiari syndrome in humans is a rare clinical condition (11, 12). In this study, we determined full obstruction in both vena cava caudalis and hepatic vein in the intrahepatic region (Fig. 2 and Fig. 3), called the Budd-Chiari syndrome, by ultrasonographic examination similarly as other studies (3, 9).
Liver damage may be increased by oxidative stress. Oxidative stress has an important role in the pathogenesis of viral hepatitis, sepsis and bacterial infections (13, 14). Liver enzymes (ALT, AST, GGT), oxidative stress index-OSI and TOS increases are marked in animals with fascielosis, while TAS decreases in serum and plasma samples (15). In this study, the levels of TAS and TOS were increased in the peritoneal fluid compared with serum samples (Table 3) and some data supported our findings (14, 16). On the other hand, the level of enzymes was increased at the beginning of treatment, particularly parenchymal enzymes, reported by Braun (17).
The response to medical therapy in the case of BCS is generally poor. The effect of diuretic therapy is uncertain (18). We used L-carnitine as liver-protection, a low salt diet and diuretic treatment. Prescribed therapy improved the condition and the quality of life of the cat, but for a short time, until the end of the therapy.
L-carnitine metabolism is impaired in patients with hepatic impairment. Deficiency of L-carnitine might be a secondary factor for liver injuries (19, 20). It is reported that L-carnitine has protective effects on liver with its potent free radical scavenging and antioxidant actions against oxidative damage in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury (21). L-carnitine was administered during the time of treatment, and weekly liver enzyme analysis was performed. The liver enzyme concentrations were decreased during the time of treatment. L-carnitine might improve liver damage, and might prolong the survival time with liver protection effect.
CONCLUSION
In summary, thrombosis of vena cava caudalis, also known as BCS, was described for the first time in a domestic cat in Turkey. Ultrasound can be used as reliable non-invasive diagnostic method for detecting BCS. Furthermore, in the cat with BCS, the use of L-carnitine which has hepatoprotective effects was beneficial as supportive treatment. Medical treatment for BCS was not completely effective, only surgical removing of occlusion ensured normal bloodstream in vena cava caudalis. This study will be of great importance for future studies, diagnosis and “treatments” of BCS in animals.